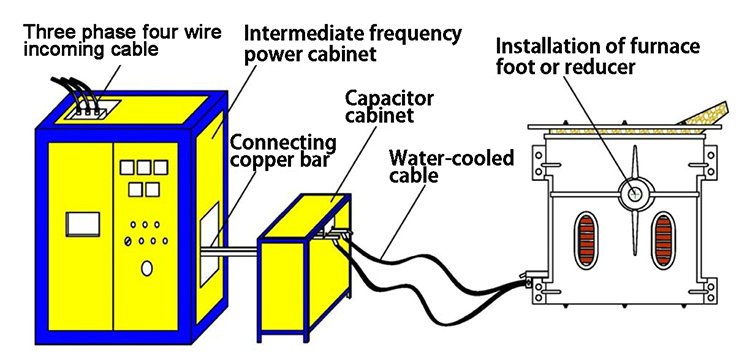
Induction furnaces are heating devices widely used in industrial production. Its working principle is based on the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction, which can convert electrial energy into heat energy for heating metals and other conductive materials. This article will provide an in-depth look at how induction furnaces work, where they are used, as well as their advantages and disadvantages.
Working principle of the induction furnace
The core principle of an induction furnace is electromagnetic induction, and its basic structure includes a main induction coil (also called a working coil) and a power coil for power supply. Induction coils are usually made of conductive material that is wrapped in insulating material to form a coil. The power coil is usually powered by an AC power source, which generates a changing magnetic field through the induction coil.
When the power coil is energized, the alternating current it produces creates an alternating magnetic field within the induction coil. This alternating magnetic field passes through the metal or other conductive material surrounding the induction coil, and according to Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, the change in the magnetic field induces eddy currents (also known as induced currents) in the conductor. The creation of eddy currents results in the heating of the material as electrical resistance converts electrical energy into heat.
Key parameters of an induction furnace include frequency, power supply power, and work coil design. High-frequency induction furnaces are generally used to heat shallow metal parts, while low-frequency induction furnaces are suitable for deep heating. The power of the power supply determines the heating speed and the height reached by the temperature, while the design of the working coil depends on the shape and size of the heated material.
Application field of induction furnace
Induction furnaces are widely used in many industrial fields, mainly including the following aspects:
- Metal heating and melting: Induction furnaces can be used to heat metal workpieces for processes such as quenching, tempering, melting, and casting. This is very common in the metalworking and foundry industries, such as making auto parts, pipes, aero engine parts, etc.
- Hardening and quenching: The induction furnace can heat the metal parts to a high temperature in a short period, and then cool them down rapidly to achieve hardening and quenching. This improves the hardness and wear resistance of the part, which is often used in the manufacture of knives, bearings gears, etc.
- Welding: Induction furnaces can be used for induction heating of welding materials such as pipes, pipe joints, and cable connections. It provides fast, uniform heating, which reduces stress and distortion and improves weld quality.
- Induction Furnace Melting: Induction furnaces are also used for melting high-temperature metals and alloys, such as for the production of special steel, alloy castings, and electronic components.
- Heat treatment: Induction furnaces can be used to heat treat metal parts to improve their mechanical properties. This is useful in manufacturing aerospace components, construction machinery, and medical equipment, among other things.
- Medical equipment manufacturing: Induction furnaces are also used in the manufacture of medical equipment, such as artificial joints, cardiac pacemakers, and dental instruments.
- Advantages and disadvantages of induction furnace

Induction furnaces have many advantages, but there are also some limitations
Advantage:
- High efficiency: The induction furnace can achieve high temperatures in a short time, so the heating speed is fast and the energy consumption is low.
- Uniform heating: The induction furnace provides uniform heating, which reduces the deformation and stress of materials and improves product quality.
- Environmental protection: Compared with the traditional gas furnace, the induction furnace does not produce waste gas and waste residue, so it is more environmentally friendly.
- Flexibility: Induction furnaces are suitable for workpieces of various shapes and sizes, and can be custom-designed as required.
- Automation: The induction furnace can be integrated with the automation system to realize automatic control and monitoring and improve production efficiency.
Shortcoming:
- High cost: The equipment cost of an induction furnace is relatively high, especially the induction furnace with high power and special applications.
- Material limitations: Induction furnaces can only heat conductive materials, not non-conductive materials.
- Frequency selection: Selecting the proper frequency is critical for different materials and applications and requires expertise.
- Maintenance requirements: Induction furnaces require regular maintenance, including inspection and repair of cooling systems, power coils, and other components.

Summarize
Induction furnace is an efficient, uniform and environmentally friendly heating equipment, which is widely used in industrial fields such as metal processing, smelting, welding and heat treatment. Although it has some limitations and cost factors, its advantages make it an indispensable part of modern industrial production, and it is expected to continue to develop and improve in the future.
Release Time: September 8, 2023
